Adapted by Nelson Nuñez-Rodriguez
Conditions of Use:

Unless otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Chapters derived from:
By David W. Ball
 Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
CC BY-NC-SA
Click on the printer icon at the bottom of the screen
![]()
Make sure that your printout includes all content from the page. If it doesn't, try opening this guide in a different browser and printing from there (sometimes Internet Explorer works better, sometimes Chrome, sometimes Firefox, etc.).
If the above process produces printouts with errors or overlapping text or images, try this method:
Click here to return to Chapter 8
| QUESTION | ANSWER |
|
1. Explain why iron and copper have the same Lewis electron dot diagram when they have different numbers of electrons. |
1. Iron has d electrons that typically are not shown on Lewis electron dot diagrams. |
|
3. Based on the known trends, what ionic compound from the first column of the periodic table and the next-to-last column of the periodic table should have the highest lattice energy? |
3. LiF |
|
5. P2 is not a stable form of phosphorus, but if it were, what would be its likely Lewis electron dot diagram? |
5. It would be like N2: 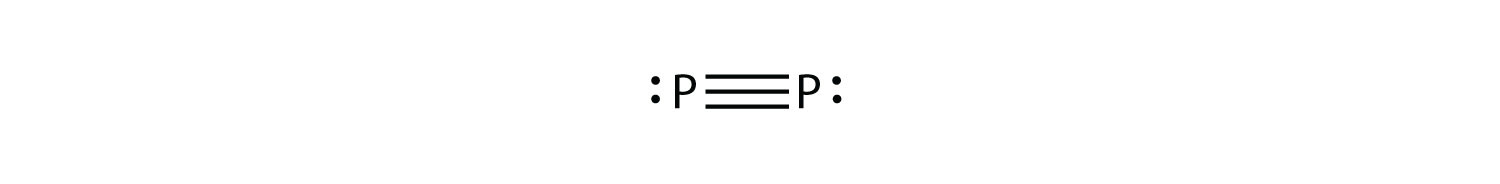 |
|
7. What are the Lewis electron dot diagrams of SO2, SO3, and SO42−? |
7. 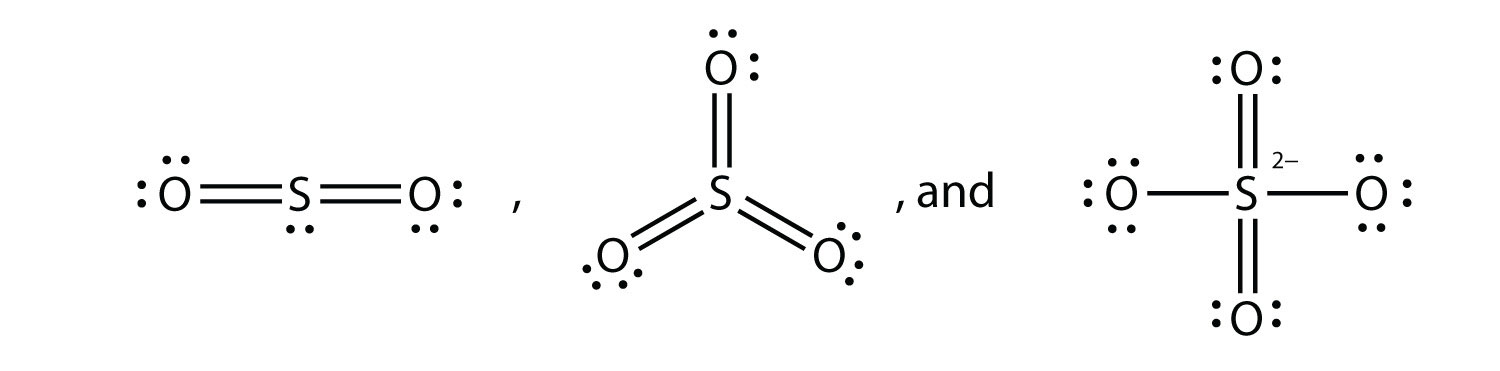 |
|
9. Which bond do you expect to be more polar—an O–H bond or an N–H bond? |
9. an O–H bond |
|
11. Use bond energies to estimate the energy change of this reaction. C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O |
11. −2,000 kJ |
|
13. Ethylene (C2H4) has two central atoms. Determine the geometry around each central atom and the shape of the overall molecule. |
13. trigonal planar about both central C atoms |
Library Info and Research Help | reflibrarian@hostos.cuny.edu (718) 518-4215
Loans or Fines | circ@hostos.cuny.edu (718) 518-4222
475 Grand Concourse (A Building), Room 308, Bronx, NY 10451
