Adapted by Nelson Nuñez-Rodriguez
Conditions of Use:

Unless otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Chapters derived from:
By David W. Ball
 Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
CC BY-NC-SA
Click on the printer icon at the bottom of the screen
![]()
Make sure that your printout includes all content from the page. If it doesn't, try opening this guide in a different browser and printing from there (sometimes Internet Explorer works better, sometimes Chrome, sometimes Firefox, etc.).
If the above process produces printouts with errors or overlapping text or images, try this method:
Click here to return to Chapter 13
| QUESTION | ANSWER |
|
1. Define hydrocarbon. What are the two general types of hydrocarbons? |
1. an organic compound composed of only carbon and hydrogen; aliphatic hydrocarbons and aromatic hydrocarbons |
|
3. Indicate whether each molecule is an aliphatic or an aromatic hydrocarbon; if aliphatic, identify the molecule as an alkane, an alkene, or an alkyne. |
3.
|
|
5. Indicate whether each molecule is an aliphatic or an aromatic hydrocarbon; if aliphatic, identify the molecule as an alkane, an alkene, or an alkyne. |
5.
|
|
7. Name and draw the structural formulas for the four smallest alkanes. |
7.
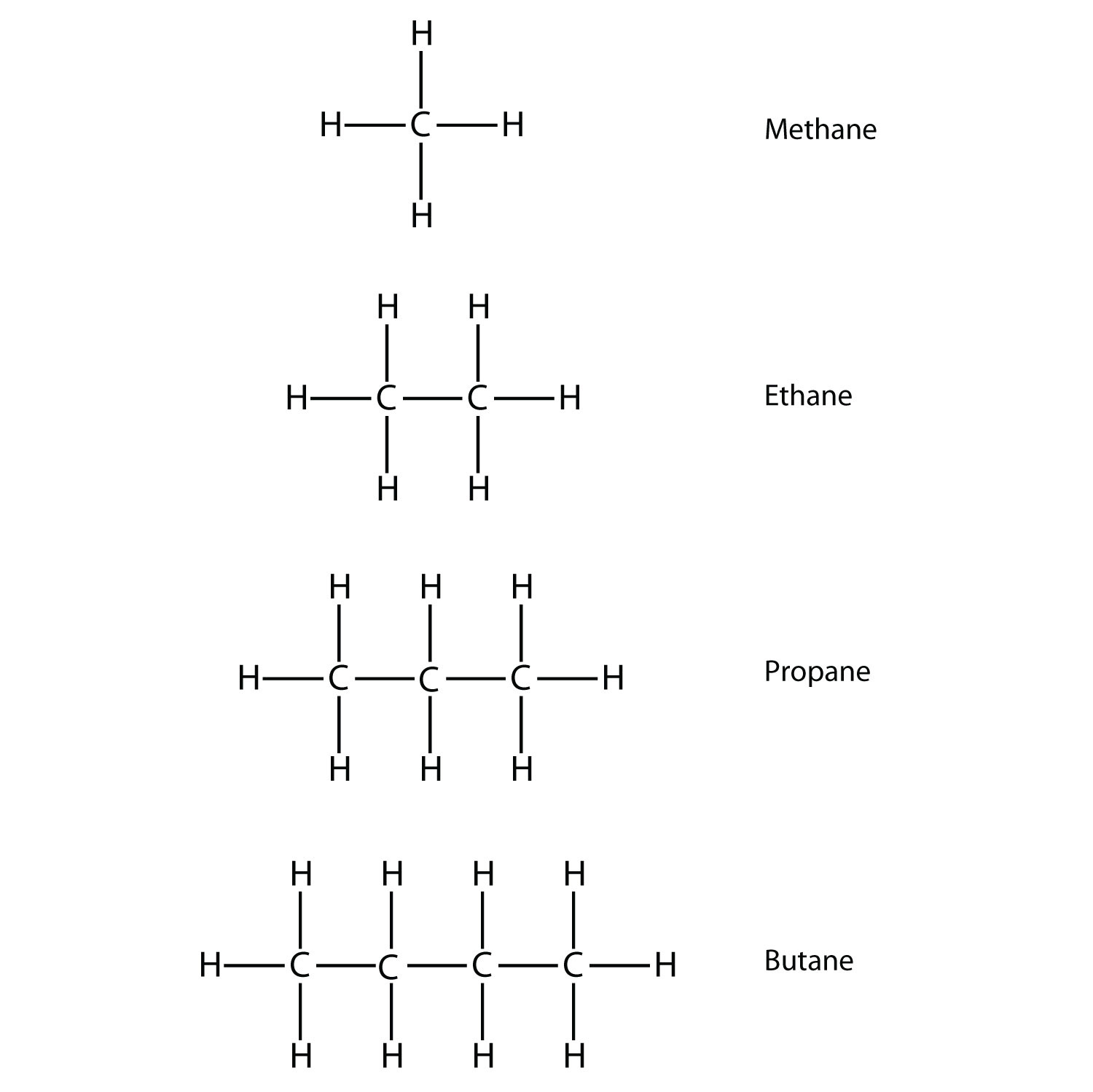 |
|
9. What does the term aromatic imply about an organic molecule? |
9. Aromatic means that the molecule has a benzene ring. |
|
11. Explain why the name 1-propene is incorrect. What is the proper name for this molecule? |
11. The 1 is not necessary. The name of the compound is simply propene. |
|
13. Name and draw the structural formula of each isomer of pentene.
|
13.
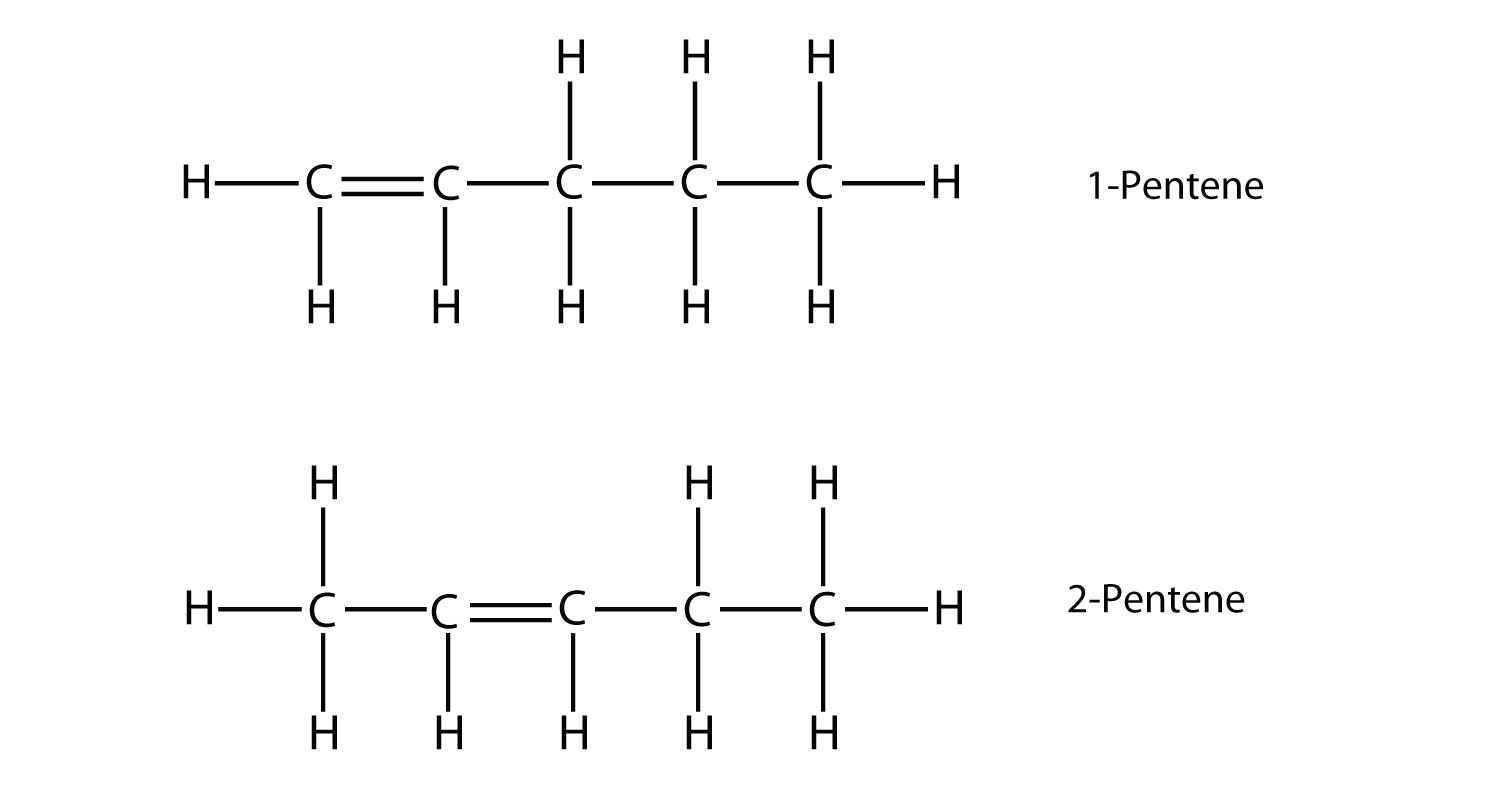 |
|
15. Write a chemical equation for the reaction between methane and bromine. |
15. CH4 + Br2 → CH3Br + HBr |
|
17. Draw the structure of the product of the reaction of bromine with propene. |
17.
|
|
19. Draw the structure of the product of the reaction of hydrogen with 1-butene. |
19. 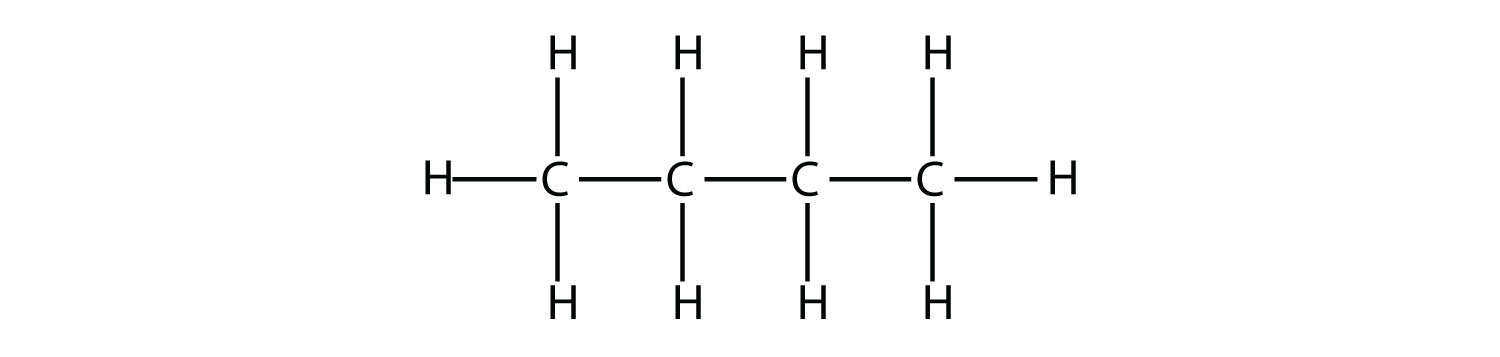 |
|
21. Write the balanced chemical equation for the combustion of heptane. |
21. C7H16 + 11O2 → 7CO2 + 8H2O |
Library Info and Research Help | reflibrarian@hostos.cuny.edu (718) 518-4215
Loans or Fines | circ@hostos.cuny.edu (718) 518-4222
475 Grand Concourse (A Building), Room 308, Bronx, NY 10451
